Metallic gold reduces tendency towards programmed cell death after experimental brain injury
Brain injury may result in chronic inflammation and neurodegeneration. Due to the anti-inflammatory effects of gold the authors have investigated the cerebral effects of metallic gold particles (20–45
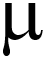 m) following a local brain injury (freeze-lesion) in mice. After 1–2 weeks it was seen that gold treatment significantly reduces the cerebral levels of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF m) following a local brain injury (freeze-lesion) in mice. After 1–2 weeks it was seen that gold treatment significantly reduces the cerebral levels of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF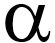 ) [a signalling substance that regulates the activity of various immune cells], oxidative DNA damage and pro-apoptotic markers [enzymes/proteins stimulating cell death] in comparison to the control results. The authors therefore consider gold particles as a tool to modulate the response to brain injury. ) [a signalling substance that regulates the activity of various immune cells], oxidative DNA damage and pro-apoptotic markers [enzymes/proteins stimulating cell death] in comparison to the control results. The authors therefore consider gold particles as a tool to modulate the response to brain injury.
Proceed to study ...
|
|